Skin and Coat: Fungal
Skin and Coat Quicklinks
Different Species of Skin Fungus
Colonies of different fungus species can cause localized or generalized forms of disease in dogs. As far as the Integumentary system (skin) or problems related to the skin is concerned, four species are of most concern:
- Microsporum
& Trichophyton:
Dermatophytosism, canine ring worm, or dermatomycosis are
skin diseases
is caused by microsproum & trichophyton fungi. These species
may be M. Canis, M. Gypseum, & T. mentagrophytes. Amongst dog
skin fungi, these species are most common. It is estimated that 70% of
dogs infected with dermal infections due to fungus are caused by
microsporum and trichophytons.
Scattered lesions on the skin with the loss of hair and scaling are common signs for this condition. Scales usually are inflamed at the margins (edges) and crust may also develop. Itching and irritation is common in severe infections. Lesions on skin develop in the shape of a ring, from the center to the periphery.
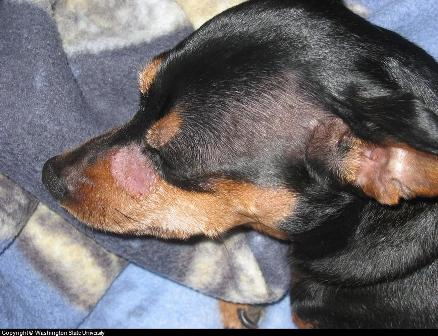
Skin Fungus on Face caused by Canine Ringworm (dermatophyte) on face of 9 year old Miniature Pincher
Source: Washington State University - Blastomyces Dermatitidis: Blastomyces dermatitidis is another fungus which causes systemic fungal infection called blastomycosis. It causes infection in that is seen in three different forms, cutaneous, pulmonary (heart) & ocular (eye). The cutaneous form of infection is related to the skin of dog. Small papules, scaly lesions which are usually ulcerated, swelling of deeper soft tissues of skin and bones are common signs for blastomycosis. Actinomyces Vicosus:
- Actinomyosis is a generalized form of fungal infection caused by Actinomyces vicosus species in dogs. Along with other systemic problems the skin is also affected. The head and particularly the skin of the nasal cavity and mouth are more susceptible to this type of dog skin fungus. Signs of skin lesions may include abscesses at nasal & mouth skin with granules in it. These abscesses have fistulous tracts in them & granular exudates may flow from it, with swelling at nose and mouth of affected dog.
- Cryptococcus
Neoformans:
Cryptococcus neoformans is a specie of fungus which can cause lameness
and lesions in skin soft tissues . This specie also causes a systemic
form of disease which primarily affects the central nervous system
(CNS), Respiratory system and integumentary system (skin).
On skin, the fungus may cause severe lesions, which are characterized by clear and brown exudates (puss which oozes from the lesions). A high degree of ulceration in the soft tissues of the skin is also a major sign that this specie is the cause.
Diagnosis and/or Identification:
For different conditions caused by dog skin fungus, it is necessary to check with the dog owner for a history of trauma or injury. Moreover clinical signs may represent the presence of a particular specie of fungus.
Culturing of fungus, collected from skin lesions, crusts or respiratory exudates is the only option to confirm a specie of fungus which is causing a systemic or localized fungus problem in dogs.
Systemic affection of these species towards different organs and types of tissues is also helpful in identifying and differentiating these species and infections. Skin lesions representing signs of cryptococcosis will also show signs of lameness, cough and a nervous system problem such as coordination. Similarly, granular skin lesions in dogs will also show some respiratory system involvement as well, indicating actinomycosis.
Treatment of Conditions Caused by Fungus:
Use of anti–fungal drugs and management of symptoms caused by the dog skin fungus are both parts of any treatment plan.
Different anti–fungal drugs can be used for different species of canine skin fungus.
Flucanozole with a dose of 2 – 10 mg/Kg/day or itraconazole at 10 mg/Kg/day is the drug of choice for cryptococcosis. Amphotericin is an alternative anti-fungal that may be used diluted 0.45% to 500ml of normal saline solution, administered every 2nd – 3rd weeks until recovery is achieved. It is also effective on the Cryptococcus species.
For Dermatophytosis or ring worm disease, shampooing using a product such as Espree Natural , followed by a rinse are effective. A rinse with enilconazole is very effective on microsporum species. Similarly griseofulvin can be used in dogs with dose rate of 25 – 100 mg/Kg as collective or divided doses, depending upon severity of fungal infection are very effective. Rinsing and administration of drugs should be continued at least 3 weeks or until a “negative brush scrapings test is passed.
For added support a homeopathic such as Ring-Ex can help to speed recovery from a dog skin fungus and maintain skin health after the condition is resolved
|
|