Eye: Symptoms
Dog Ear QuickLinks
Common Dog Eye Diseases:
Dog eyes can be affected by various diseases. These can be minor issues such as allergies or secondary infections, or they can be severe infections in different parts of the eyes caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites and allergens.
Similarly, non infectious dog eye diseases include conformational abnormalities, glaucoma, cataracts, opacity and atrophies (weakness). There are some congenital (inherited) canine eye diseases as well, which are retinopathies (damage to a dog retina). Dog eye cancers and dog eye tumors are the most severe type of eye diseases in dogs, and are considered to be fatal and destructive.
The following is a brief overview of a few of the major dog eye conditions:
- Dog Eye Infections: Canine
eye infections, which are infectious and that spread from
animal to animal and from one to the other eye and which progresses
over
time are
commonly known as infections. These infections in dog eyes are
specifically caused by various
species of bacteria, viruses and least commonly by fungus. Some
parasites like dog eye worms also cause diseased eyes in dogs, which
also are infectious or spreadable to other animals.
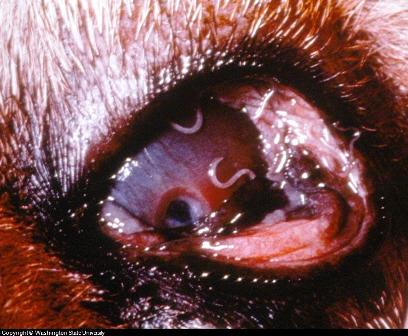
Canine Eye Diseases Photo
Dog Eye Worms
Dog eye infections can be primary or secondary in nature, i.e. they either build up within the dog eyes or are extended into the eye from infectious lesions around the eyes, i.e. face, nose or ears. Some allergens, like foreign objects, dust etc. also cause primary forms of inflammation in dog eyes, which becomes complicated due to secondary infections.
Some common examples of dog infections are conjunctivitis (Pink eye), blepharitis (Inflammation of outer eyelids), Dacryocistitis (Inflammation of tear sac), chorioretinitis (Inflammation of Choroid and Retina) and orbital cellulitis.
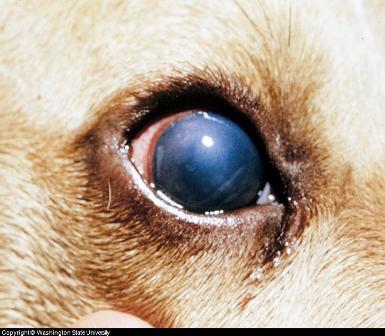
Canine Eye Disease Photos
Blue Eye Dog Infectious Hepatitis
- Conformational Abnormalities: These
types of dog eye problems include
non infectious and comparatively mechanical dog eye diseases.
Some of the conformational abnormalities in dog eyes are:
- Entropion; Dog entropion is an
inversion of some or the whole eyelid into the eye. This is one
of the most common non infectious diseases noted in dogs. Secondary
problems that are the result of dog entropion includes irritation and
the formation of secondary infections
over the surface of the affected dog eye. Surgical adjustment along
with supportive measures
are required to treat this condition.
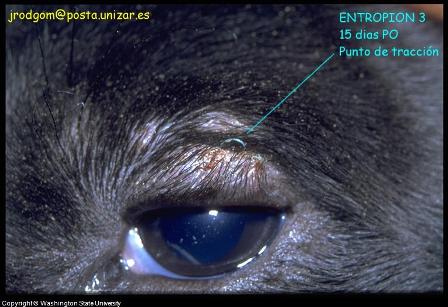
Picture Dog Eye Condition - Entropion
- Ectropion: A dog entropion is an
abnormal turning out of the inner part of the eye, In other
words, it is an everted eyelid. It occurs bilaterally (both eyes) and
some breeds
like the Bull
Mastif, Great Dane, St. Bernard and Spaniels are more prone to this
conformational dog eye abnormality. The condition results in the
conjunctiva becoming exposed to environment,
thus irritation and secondary infections are the most common
complications
related with this dog eye problem.
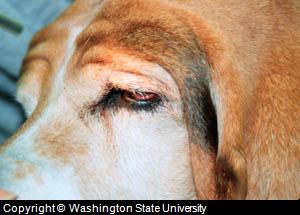
Basset hound with severe lower lid ectropion and upper entropion
- Lagophthalmos: This canine eye disease is simply the inability to close the eyelid, thus the cornea is not protected by the outer layer - the dog eyelid. This usually occurs due to mild dryness and eye trauma, facial paralysis etc. This condition leads to permanent loss of corneal function, nerve paralysis, ulcers and opthalmic lesions due to eye exposure to various pathological and physical factors.
- Disorders of Canine Cilia: Abnormalities of opthalmic cilia includes distichia (misdirected eyelashes over margin) epiphora (watery eyes) and corneal ulceration. These dog eye conditions cause severe irritation and abrasions, which turns into clinical complication such as ulcers, lesions and opthalmic parts gradually becomes necrosed (cell death).
- Entropion; Dog entropion is an
inversion of some or the whole eyelid into the eye. This is one
of the most common non infectious diseases noted in dogs. Secondary
problems that are the result of dog entropion includes irritation and
the formation of secondary infections
over the surface of the affected dog eye. Surgical adjustment along
with supportive measures
are required to treat this condition.
Other Common Dog Eye Diseases:
Along with eye disease dog infections and conformational abnormalities, there are certain other conditions, which are not truly infectious but the pathogenesis shows that some infectious, age, genetic and physical factors are involved in their occurrence.
- Canine Glaucoma: Glaucoma in dogs
is a collective term for a group of dog eye diseases, which involves an
abnormality in
the production and flow of fluids in dog eyes. Dog Glaucoma can result
in destruction of the
retina and orbital disc along with the loss of eye
functionality due to pressure. Different forms of Dog Glaucoma can be
open described as angle or closed
, i.e. progressive or acute in nature respectively. Treatment is
performed either with the use of therapeutics and initial
massage or with dog glaucoma surgery in latter stages of the disease.
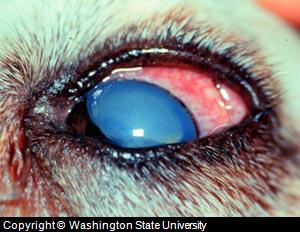
Dog Eye Diseases Picture - Dog Glaucoma Picture
- Canine Cataracts: Cataracts in dogs are related to cloudiness or opacity of the lens. This is one common dog eye disease related to the lens of the dog's eye. It usually occurs as a secondary condition to some systemic diseases such as diabetes mellitus, severe eye traumas, congenital conditions and gradual weakness of the opthalmic apparatus with age.

Geriatric Miniature Poodle Picture Dog Cataracts
- Dog Eye Tumors: One of most
complicated and hard to treat eye disease dog is dog eye cancer or a
canine eye tumor. Cancer can occur in any part of a dog
eye, but dog eye tumor problems in the outer eyelids are the most
common. Adenomas and
adenocarcinomas are the most frequently occurring eye cancers in dogs.
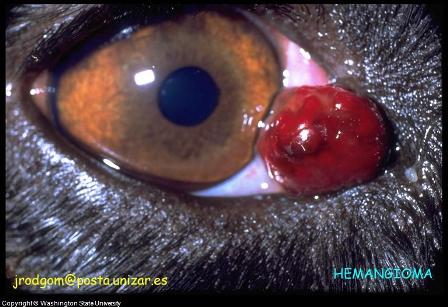
Canine Eye Diseases Photo - Hemangioma (Benign Dog Eyelid Tumor) on Third Dog Eyelid
Metastatic (spreading) types of dog eye cancers are usually secondary in nature which spreads from other parts of body to the eye. Papilloma, histioocytoma and mastocytoma are other types of dog eyelid cancers.
The retina and orbital parts of the eye are other common sites for the occurrence of dog eye cancer. These and dog eyelid cancers are treated with therapeutics, radiation and surgery. the prognosis for dog eye cancer depends upon metastasis (how fast it is spreading or has spread) and the clinical chronicity of cancer (length of time dog had disease). Metastatic dog eye cancer usually has a poor prognosis.
Management and Treatment of Dog Eye Diseases:
Dog eyes, like those of other animals and humans are very delicate organs, thus even minor irritation can turn into a complication due to severe clinical symptoms and response of the patient towards inflammation and irritation. It is thus always recommended that dog eyes should be frequently observed for any unusual symptoms and development of any progressive condition which sometimes does not show any symptom of irritation or pain at all.
Dog eye diseases should be carefully diagnosed, and then treated specifically, meaning with medications manufactured for the particular dog eye condition identified. In support, measures such as regular cleaning with an isotonic solution such as Opticlear. Be sure to select a product for dog eye cleaning that is an isotonic wash solution in the form of drops.
Natural remedies such as i-Clenz for cleaning tear stains and the area around the eye (can be used on the surface of the eye if diluted per the manufacturers directions, but an eye wash such as the Opticlear mentioned above is preferred for cleaning the surface of the eye) and the use of local eye health tonics such as Eye Heal can help to hasten recovery. Natural remedies are one way to support eye health, both in cases where there is eye disease dog and as a preventive measure.
|
|