Heart and Blood:
Heart and Blood QuickLinks
Causes of Enlarged Canine Heart:
In cardiac studies, an enlarged dog heart is specifically a stage of an underlying canine heart disease, which occurs due to congestion, inflammation or myopathies (muscular pathology) of the heart. A dog heart in this condition appears flabby and thinner, and eventually enlarged in size.
For this reason, the cardiac muscles loose strength and the pumping function of the heart is badly affected. Once the stage of enlargement occurs, it represents that clinical symptoms of canine heart disease have matured, followed by dog congestive heart failure.
Different conditions, such as parvovirus infections, dilated cardiac myopathies, heartworm disease, and taurine deficiency in the diet can lead to enlargement of a dog heart. This dog heart condition is more common in large and obese dogs, which have comparatively more fat deposition on their body.
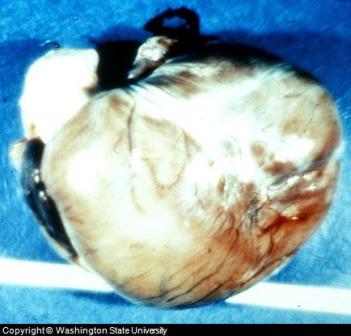
Enlarged heart due to
heartworm
Source: Washington State University From the collection of Dr. Richard
Wescott
Symptoms:
A canine enlarged heart is a literal stage of potential heart disease, which occurs along with the exhibition of heart disease symptoms. Clinically, a dog with heart disease will show symptoms such as lethargy, cough, irregular respiration, intolerance to exercise, reluctance to eat and fainting.
Symptoms such as abdominal ascites (fluid accummulation) and bloating along with frequent unconsciousness surely represents a change in dog heart anatomy. In the presence of such symptoms a dog should be suspected for enlargement heart dog, which if not attended to in a timely manner, is followed by certain dog heart failure.
That is why, in most cases, a canine enlarged heart is considered an advanced part of a dog heart condition and is declared as being fatal for a patient.
Diagnosis:
A dog showing classical symptoms of canine heart disease should immediately be referred to a veterinarian for a detailed examination. Clinical symptoms are always exhibited in advanced stages of the disease. An initial diagnosis is made on the basis of a detailed physical examination and clinical procedures such as a detailed history, detection of heart murmurs, pulses, respiratory sounds, ascites and arrhythmias. Detailed chest X-Rays, electrocardiogram and ultrasound of the heart are more specific as are advanced techniques for confirmation of dog heart enlargement and underlying heart disease.
Treatment:
Any underlying disease, whether it is an infection, cardiac-myopathy, infestation or anything, should be treated specifically. Both medical and surgical approaches to treatment may be required and for this reason, the patient should be considered as “Critical” and treated as a medical emergency.
Dog enlarged heart not only represents a critical situation for a dog, but also it is an indicator of the severity of the condition. Results of any examination and tests will reveal the anatomical and physiological status of the heart, indicating what supportive and symptomatic care is thus needed.
Different drugs and heart tonics are usually preferred, such as diuretics, Digitalis, cardiac muscle constrictors and natural tonics along with supportive dietary supplements are used for improving the dog's condition. Specific tonics to consider include Circulation Tonic. If the heart congestion and enlargement is due to hearworm, then try Parasite Dr, but only if discussed with your veterinarian first. At home, for a dog with heart disease and an enlarged heart diagnosis, care should be taken in the dog's daily routine. The dog should not be allowed to jump, run or chase. Similarly, a dog heart diet should not contain extra fats. A simple diet is always better for a canine heart patient. If required, taurine should be added for heart strength.
|
|